|
|
Molecule of the Month May 2009 |
|
|
Oligopyrenotides - Abiotic Foldamers with Nucleic Acid-Like Structural Properties |
||
|
||
|
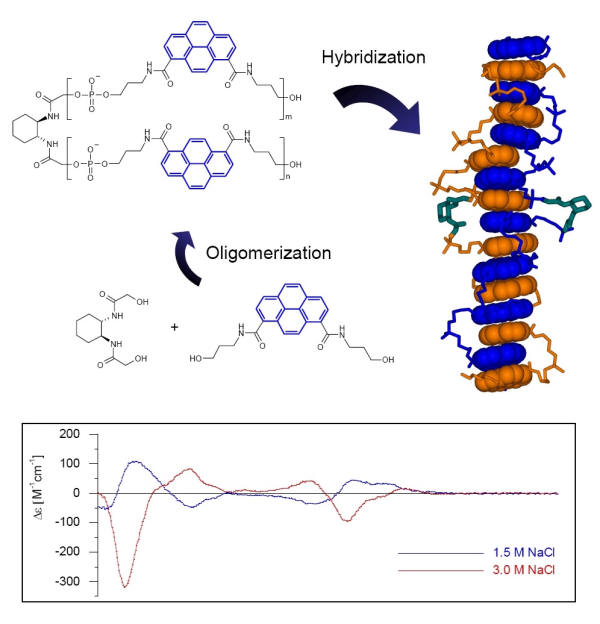
Oligopyrenotides are composed of achiral, phosphodiester-linked pyrene building blocks and a single chiral 1,2-diaminocyclohexane unit. Oligomers form stable hybrids in aqueous solution. Hybridisation is based on stacking interactions of the pyrene building blocks. Hybrids display salt concentration-dependent, structural polymorphism. They adopt left- or right-handed double helical conformations, depending on the salt concentration.
This work was carried out in the group of Prof. Robert Häner. References:
|
||