|
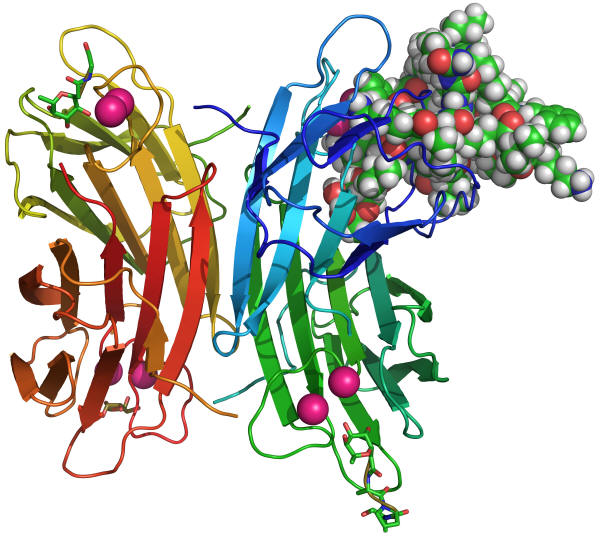
The picture shows a model of the bacterial lectin Lec B dimer (in ribbon diagram) complexed with FD2 (cpk model), a glycopeptide dendrimer identified by combinatorial screening and which inhibits the formation of biofilms in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
The effect is observed on several antibiotic resistant strains of this dangerous human pathogen, and suggests a new therapeutic approach to treat P. aeruginosa infections.
This work was carried out in the group of Prof. Jean-Louis Reymond.
References:
-
E. M. V. Johansson, S. A. Crusz, E. Kolomiets, L. Buts, R. U. Kadam, M. Cacciarini, K.-M. Bartels, S. P. Diggle, M. Cámara, P. Williams, R. Loris, C. Nativi, F. Rosenau, K.-E. Jaeger, T. Darbre, J.-L. Reymond;
"Inhibition and Dispersion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms by Glycopeptide Dendrimers Targeting the Fucose-Specific Lectin LecB"
Chem. Biol., 15, 1249-1257, (2008);
doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.10.009.
-
E. Kolomiets, M. A. Swiderska, R. U. Kadam, E. M. V. Johansson, K.-E. Jaeger, T. Darbre, J.-L. Reymond;
"Glycopeptide Dendrimers with High Affinity for the Fucose-Binding Lectin LecB from Pseudomonas aeruginosa"
ChemMedChem, 4, 565-569, (2009);
doi:10.1002/cmdc.200800380.
-
Kai-Jye Lou;
"Breaking the biofilm barrier"
SciBX, 2, No. 4, (2009);
doi:10.1038/scibx.2009.124.
|